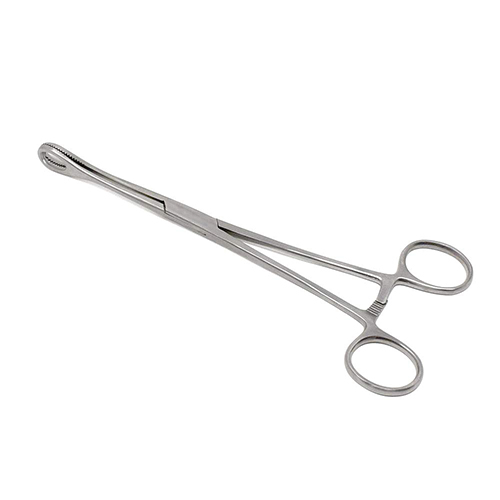
Surgical sponge-holding forceps come in various sizes and shapes, depending on the specific requirements of the procedure. Some of the common types include curved and straight forceps, each offering different levels of access to the surgical site. The curved variety is particularly useful for reaching deeper or more confined spaces in the body, while straight forceps are typically used for more accessible areas.
These forceps are essential for maintaining a clean surgical field. Surgeons often use them to place or remove sponges soaked with blood, fluids, or antiseptics. By using sponge-holding forceps, the surgical team can keep the patient’s wound clear, aiding in better visibility and reducing the risk of infection.
Another crucial function of these forceps is preventing sponges from being left inside the patient’s body, which can lead to severe post-operative complications. The use of radiopaque sponges (sponges visible on X-rays) further helps prevent such accidents, especially in combination with counting protocols and tools like sponge-holding forceps.
The forceps are generally designed to be ergonomic, offering a comfortable grip for the surgeon and reducing hand fatigue during lengthy procedures. They can be locked in position, providing constant pressure without requiring the surgeon to maintain a continuous grip. Some models feature ratchet mechanisms that allow incremental adjustments to the pressure applied to the sponge, providing greater control during delicate tasks.
In summary, sponge-holding forceps are indispensable in ensuring that surgical procedures are both clean and precise. Their ability to safely and efficiently manipulate sponges contributes to better surgical outcomes, while their design promotes ease of use and reliability for the operating team.














There are no reviews yet.